Firstly I worked out how I wanted to make the invite interactive as this would need to match alongside the exhibition.
So I thought about a simple fold that would make in the invite into an interesting layout and shape. Also, maybe give them a little gift to get them thinking about the exhibition and make them want to investigate with the paper crane...
So i have come up with the idea of a diamond shape as this is the outline of a Celtic knot. Again making the connection with luck and the Irish.
I ripped a piece of A3 paper in half and folded from the centre to make a diamond shape....
I noticed that I could folded the edges in to make a gate fold and therefore the information inside would be sealed with a grand opening of the two sides. This was just a happy accident.
So this is what it would look like if it was folded in... I like this because the idea that the information is concealed and therefore people will wonder what is inside so they will make the initial interaction. Also it is small, compact and can be stored/stacked easily.
This would open like this so I could follow the creases of the paper for my layout, following the aesthetic of the back of my poster...
So I created a simple template on illustrator to follow to make sure all the elements worked. I thought using the same title as the poster and the same style would create a connection and then people would be like oh that's what those invites was for... etc.. I have block coloured the diagonals as this is going to be the outside of the invite. Now to create the front, which will be divided by a gate fold.
Although this will be divided like this so that the fold can create the enclosure...
This was my initial thoughts as I thought having the charity hidden by the mini paper crane we are going to have in the middle will be a grand reveal, but then I thought this might not be a good idea people might be more inclined to read if they can see the charity logo.
So I chose to put it in the bottom left.... This is not the first things they are going to look at but at least it doesn't need something to be removed for them to see it. Also a small caption has been added to tell them a little about the age range and telling them about the concept of luck.. The how to build a paper crane will only be revealed if the invitation is fully interacted with... Therefore these are the people that will most benefit and enjoy this task...
I have put that it is around St Patrick's day this will given them some connection and therefore won't forget what date if the invitation is lost etc... I have now put how to build a paper crane underneath where the crane will be placed to give them some information as to why the paper crane is there but not in too much detail.
I have also put the date, as I realised that this would just be relating to one say if St Patrick's day was left to be the only date contact info... I have now out dots around the crane to connote that this is what the whole exhibition is about... But this is only a slight clue and not everyone will put two and two together.
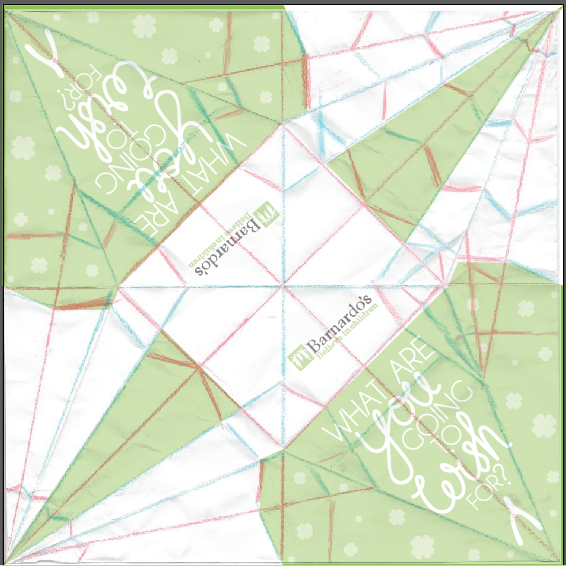
This is the final outcome, all sections have some information on them... And it all looks evenly balanced out with the focus on the paper crane.... This invite is giving away everything but nothing directly, therefore create curiosity, which is the main element to make people come and engage with the exhibition.
This is the final printed outcome....
The paper crane doesn't fully cover up the writing which I am glad about as you can see there is information underneath that needs to be revealed, therefore more people will be inclined to remove it..